No. They do not remove carbon dioxide (CO2). Almost all air purifiers are designed to capture some combination of particles and toxic gasses, but CO2 can’t be captured by the same filters that capture other gaseous air pollution. Only ventilation removes CO2.
It’s important to at least understand how CO2 might build up in your home, what kinds of problems it may cause, and how you can manage it. Read on to learn more about CO2 in your home.
Is carbon dioxide (CO2) toxic?
Yes, CO2 is toxic.
Higher than normal levels of CO2 can change the body’s internal chemistry and prevent normal functioning, and extremely elevated levels of CO2 cause severe and sometimes fatal poisoning. In addition, CO2 accumulates in poorly ventilated areas along with viruses, chemicals, and other indoor air pollutants. So a high concentration of CO2 may mean other air pollutants are present in high concentrations as well.
Why is CO2 toxic?
When CO2 comes into contact with the water in your body it forms carbonic acid, which impairs your body’s natural chemistry.
Carbon dioxide is not toxic because it displaces oxygen, but rather because it turns your blood to acid. You may recognize carbonic acid as the slightly tangy taste on your tongue from carbonated water, but carbonic acid in your blood causes all sorts of problems. Your metabolism is very reliant on a perfect pH balance and if it changes many of the bodily processes will simply stop working. Excess CO2 can cause a condition called respiratory acidosis, the “respiratory” referring to how the CO2 can’t leave your lungs fast enough.
What are the symptoms of carbon dioxide poisoning?
The primary symptoms of CO2 poisoning are fatigue, confusion, headaches, tremors, and other neurological impacts.
Respiratory acidosis occurs when excess CO2 cannot be exhaled and is causing acid to build up in the body. This prevents your basic biochemistry from working properly. Your brain and nerves need a lot of resources to function compared to the rest of the body, so the problems that occur in the brain and nervous system are most serious– trouble thinking, dizziness, and eventually unconsciousness and death. Muscle spasms, bowel distress, and heart palpitations are also common symptoms.

What level of CO2 is toxic to humans?
Carbon dioxide may cause unconsciousness and death at 40,000 ppm, but may affect decision making as low as 1,000 ppm.
Outdoor carbon dioxide (CO2) levels have been increased by human activity to an average of 412 ppm (0.04%) from 318 ppm about a hundred years ago, and closer to 550 ppm near roads. Up to 3,000 ppm is considered safe for working conditions in the US. Around 40,000 ppm is where we start to worry about long term injury and death. However, recent research has uncovered that our decision making starts to falter at relatively low levels- 1,000 ppm or just 0.1% CO2, which could easily happen by just sitting indoors with the windows closed. Leading indoor air quality expert Joseph Allen estimates that just doubling ventilation can increase individual productivity by an average of $6,500 a year.
Can carbon filters remove CO2?
No, ordinary carbon filters cannot remove CO2.
The media inside carbon, charcoal, or activated carbon filters is cheap and readily available because it is generally made from wood and other plant material like coconut husks. Carbon filtration works because plants, like us, are carbon-based. Air and water pollutants like mold spores, bacteria, and many chemicals are also carbon-based, and this mutual chemistry allows pollution to disrupt our body’s natural processes.
CO2 is a little different as a pollutant because we can’t fool it into attacking carbon filters instead of our bodies. It is released as a stable end product of our metabolism and doesn’t disrupt natural processes with mutual carbon-based reactions. CO2 is still a chemical, and can be goaded into attacking and sticking to very specific air filter additives, but these additives don’t grow on trees like carbon, so are expensive and typically only used for special purposes like industry or in submarines.
Do plants remove carbon dioxide?
Yes, but not enough.
We are all familiar with photosynthesis and how plants use air and sunlight to absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen to grow. There is a lot more to it, but converting carbon dioxide to oxygen is most plants’ primary impact on the atmosphere. We need plants to remove carbon dioxide because as we said earlier, CO2 is more toxic than oxygen is vital.
The outdoor concentration of CO2 is around 0.04% and just four times that level can impact decision making. Outdoor oxygen is usually 21% and needs to be no less than 19.5% for normal breathing and no less than 16% to do strenuous activity. When you breathe, CO2 and oxygen change at the same rate because one molecule of oxygen in is one molecule of CO2 out. So using up enough oxygen to drop the level 5% will make you tired, but the increase of 5% CO2 could be deadly. Clearly CO2 is the issue here.
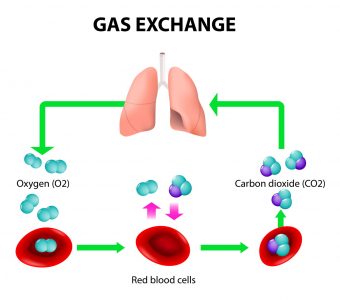
One oxygen molecule is traded for one carbon dioxide molecule
Plants “breathe” more slowly than we do because they don’t need energy to move around. This article breaks down how to calculate how many plants you would need to have a self-sustaining personal atmosphere and it’s about 700 average-sized houseplants per person. Also, depending on the plant it may not remove carbon dioxide without light.
How do I remove carbon dioxide from my home?
Opening the window is one of the best ways to bring in fresh air and decrease CO2. Mechanical ventilation such as HVAC can also bring in outside air.
Just opening the window for about seven minutes can replace half the air in a room and drop CO2 levels halfway toward lower outdoor concentrations. If it is an option, activate the vent or fan option on your HVAC to bring in outside air. Finding yourself feeling sluggish or tired after spending time in a certain room could be due to CO2 building up from poor ventilation. For consistent problems or just simple curiosity, get a CO2 monitor for around $30 to find out how bad the CO2- and ventilation- is where you are.
Keep an eye on this blog to learn more about how to keep your indoor air quality at its best. Also watch our Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter accounts for everything else on the science of clean air.







